This historical German designation indicates the composition of a cable. To understand how a cable with a VDE designation is made up and what its characteristics are, it is sufficient to refer to the codes that make up the designation: each code corresponds to a particular feature of the cable.


The history of the VDE
The VDE Association was founded in 1893 in Germany as the "Association of German Electrical Engineers" (Verband Deutscher Elektrotechniker) and currently has over 35,000 members.
The aim of the association is to encourage the sharing of technical knowledge, to support the use of this technology in various fields including industry, and to certify the safety and quality of products and components by means of tests and certification marks.
Cables according to VDE
Driven by the strong industrialisation of Germany, the VDE developed various cable construction standards. These cables quickly became the standard in Europe.
The historical codification of their names indicates how the cable is composed, each code characterising a particular feature of the cable. One example is the VDE 812 standard for communication and data cables.
NF coding, CENELEC coding, are different coding systems to determine the characteristics of a cable
To find out more, our article Understanding cable names explains their marking and how they are made up.
Example with CAE GROUPE cables
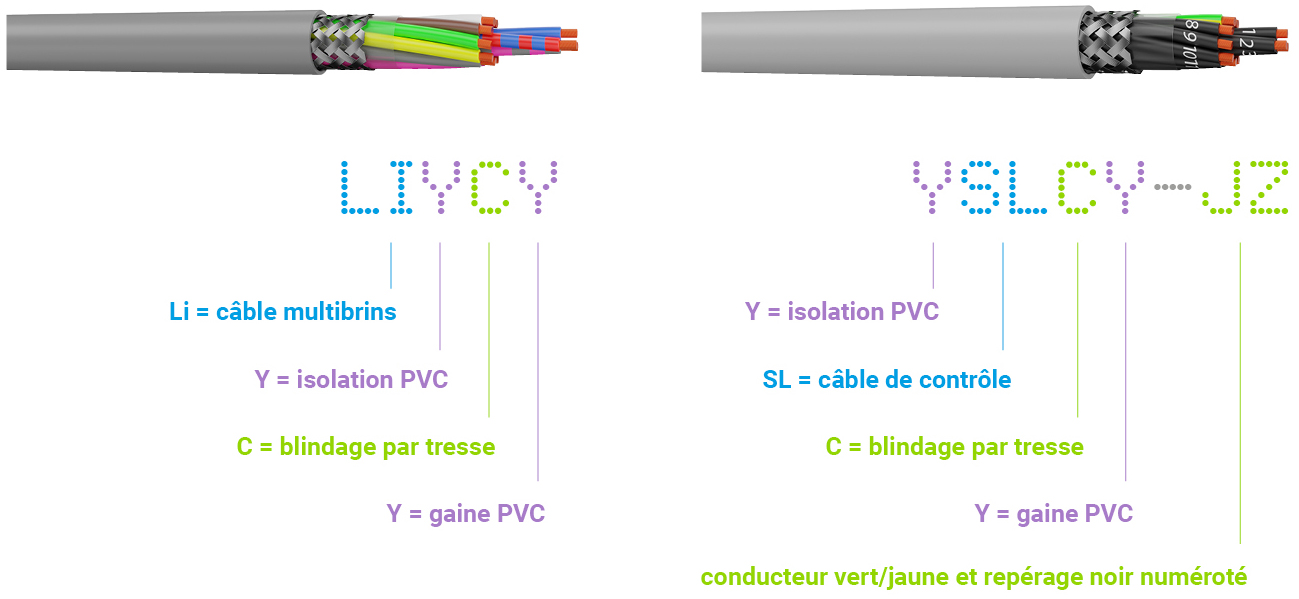

VDE code
|
INSULATION AND SHEATHING MATERIAL |
|
|---|---|
| Y | PVC |
| 2Y | PE |
| 2X | Cross-linked PE |
| H |
Halogen free |
| 6Y |
FEP (fluorinated Ethylene Propylene) |
| 7Y |
ETFE (Tetra fluoro ethylene) |
| 11Y |
PUR (Polyurethane) |
|
CABLE DESIGNATION |
|
| Li | Stranded wire (according to VDE 812) |
| SL |
Controle cable |
| Si |
Silicone wire or cable |
| AF |
Flexible core for single conductor |
| GL |
Glass fibre braid |
| FL |
Flat cable |
|
SPECIAL FEATURES |
|
| Ö | Oil resistant |
| C | Braid shielding |
| D | Shielding by covering |
| S | Steel braid armouring |
| U | Non-flame propagating |
| W | High temperature |
| O | Without protective conductor (Green/Yellow) |
| J | With protective conductor (Green/Yellow) |
| Z | Numbered conductor |